Which of the Following Is a Carbon Sink Quizlet
Many CO 2 molecules that diffuse into sea surface waters diffuse back to the atmosphere on very short time scales. Oceans are considered the main natural carbon sinks as they are capable of absorbing about 50 of the carbon emitted into the atmosphere.

Term 3 Carbon Cycle Diagram Quizlet
A carbon dioxide CO2 sink is a carbon reservoir that is increasing in size and is the opposite of a carbon source.

. Which one of the following statements is true. Oceans and the Carbon Cycle Part A. Green plants play a very important role in the.
Following are the major steps involved in the process of the carbon cycle. Tropical forests are taking up less carbon dioxide from the air reducing their ability to act as carbon sinks and bringing closer the prospect of accelerating climate breakdown. The ocean is another example of a carbon sink absorbing a large amount of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
The movement of carbon among Earths spheres as diagrammed below is known as the carbon cycle. Click card to see definition. The cost per unit of water consumption with an increasing block rate structure Increases with additional units of consumption.
There is a variance on how much the peatlands act as a carbon sink or carbon source that can be linked to varying climates in different areas of the world and different times of the year. What is really important to know is how much more carbon is taken up by. Down to the Deep - The Oceans Biological Pump.
These animals and plants eventually die and upon decomposing carbon is released back into the atmosphere. These are the reservoirs or sinks through which carbon cycles. Oceans have a large capacity to absorb CO 2 thus reducing the amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere and bringing carbon atoms into the ocean system.
The main natural carbon sinks are plants the ocean and soil. Oceans are the main carbon sinks and absorb up to 50 of CO2. Carbon dioxide sink.
In Part 1 of this lab you learned that green plants within the terrestrial biosphere can act both as a carbon sink as they turn CO 2 and water into carbohydrates through photosynthesis and as a carbon source as they respire CO 2 produced by the metabolism of carbohydrates when the plants need energy. Public awareness of the significance of CO 2 sinks has grown since. Forests oceans and soil are all natural carbon sinks which absorb carbon dioxide from the world around them Trees specifically absorb as much as 20 tons of carbon dioxide per hectare each year.
One of the largest unknowns in our understanding of the greenhouse effect is the role of the oceans as a carbon sink. The ocean takes in 92 Gtyear and gives off about 90 Gtyear making the ocean a net carbon sink. 1 Gigatonne or metric gigaton unit of mass is equal to 1000000000 metric tons.
Tap card to see definition. Tap again to see term. Carbon stores are where carbon-containing compounds are held for an indefinite period of time.
When the accumulation of carbon is greater the site is a carbon sink as on the whole the forest is removing CO. They continually take carbon out of the atmosphere through the process of photosynthesis. As carbon dioxide CO 2 in the atmosphere sugars or carbohydrates C n H 2n O n in living organisms and calcium carbonate CaCO 3 in rocks and.
Scientists are interested in stored carbon also known as sinks or sequestrations because long-term carbon storage in vegetation and soils are two ways of mitigating CO 2 a greenhouse gas. Peat bogs act as a sink for carbon because they accumulate partially decayed biomass that would otherwise continue to decay completely. Carbon present in the atmosphere is absorbed by plants for photosynthesis.
Forests are typically carbon sinks places that absorb more carbon than they release. The oceans cover over 70 of the Earths surface and play a. The carbon cycle forms an important part of life on Earth and the way in which living things interact with one another.
The oceans are the Earths largest carbon reservoirs. The arrows show how carbon moves among Earths spheres. However new evidence suggests this figure could be even higher.
The ocean is a giant carbon sink that absorbs carbon. Marine organisms from marsh plants to fish from seaweed to birds also produce carbon through living and dying. Plants grab carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to use in photosynthesis.
Which Statement Is A Function Of Photosynthesis Quizlet. The ocean is a giant carbon sink that absorbs carbon. More than half of the carbon sink in the worlds forests is in areas where the trees are relatively young --.
The ocean is one of Earths natural carbon sinks taking in carbon dioxide and other forms of carbon from the atmosphere. See carbon cycle for more detail. Forests are typically carbon sinks places that absorb more carbon than they release.
Some of this carbon is transferred to soil as plants die and. Globally the two most important carbon sinks are vegetation and the ocean. The main natural sinks are the oceans and plants and.
The decomposition and plant metabolism. Most carbon is stored in rocks and sediments while the rest is stored in the ocean atmosphere and living organisms. In particular plankton corals fish algae and other photosynthetic bacteria are responsible for this capture.
The Aral Sea in central Asia once one of the. Much of the carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere by the burning of fossil fuels is soaked up by the oceans but changes in the climate are altering this absorption in surprising ways. What are the effects of deforestation.
The black numbers in the diagram indicate how much carbon is stored in carbon sinks areas of storage in billions of tons gigatonsGtC. The deep ocean harbors 36000 gigatonnes of carbon while the waters surface contains 1020 gigatonns. Around 25 of all CO2 emissions are absorbed by the ocean making it one of the worlds largest carbon sinks.
The demand for water tends to be price inelastic for both residential and irrigation uses. When the sum of decomposition and respiration is greater the site is a carbon source as the forest is adding carbon back into the atmosphere. Click again to see term.
A carbon sink is any reservoir natural or otherwise that accumulates and stores some carbon -containing chemical compound for an indefinite period and thereby lowers the concentration of carbon dioxide CO 2 from the atmosphere. The main natural carbon sinks are plants the ocean and soil. These plants are then consumed by animals and carbon gets bioaccumulated into their bodies.
Worlds biggest terrestrial carbon sinks are found in young forests. The cutting down of trees in a large area or the destruction of forests by people.

1 B The Carbon And Water Cycles Are Systems With Inputs Outputs And Stores Flashcards Quizlet
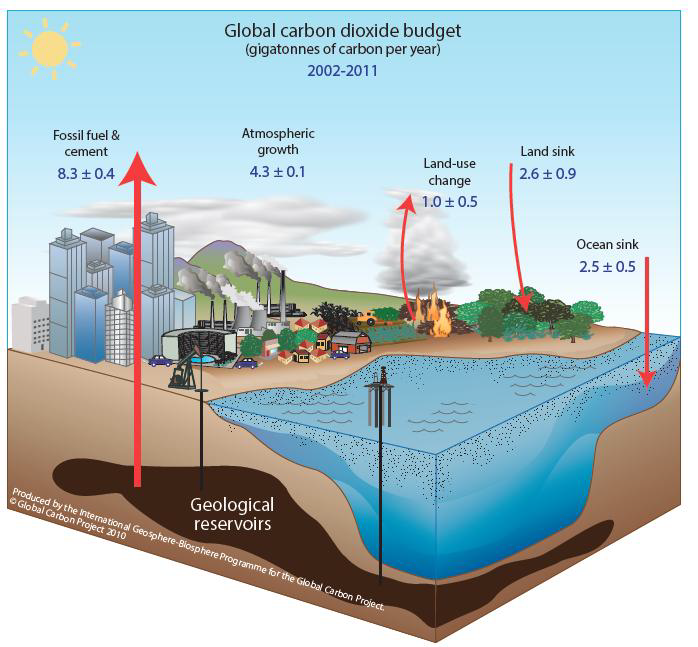
What Is The Carbon Cycle What Is The Science Behind It United States Carbon Cycle Science Program

Ap Environmental Science Test Review Flashcards Quizlet

Chemistry Environment Carbon Cycle Flashcards Quizlet

Es Unit 8 Climate Change Japanese Flashcards Quizlet

Ap Environmental Science Test Review Flashcards Quizlet

4 3 Carbon Cycling Flashcards Quizlet

Carbon Cycle Diagram Diagram Quizlet
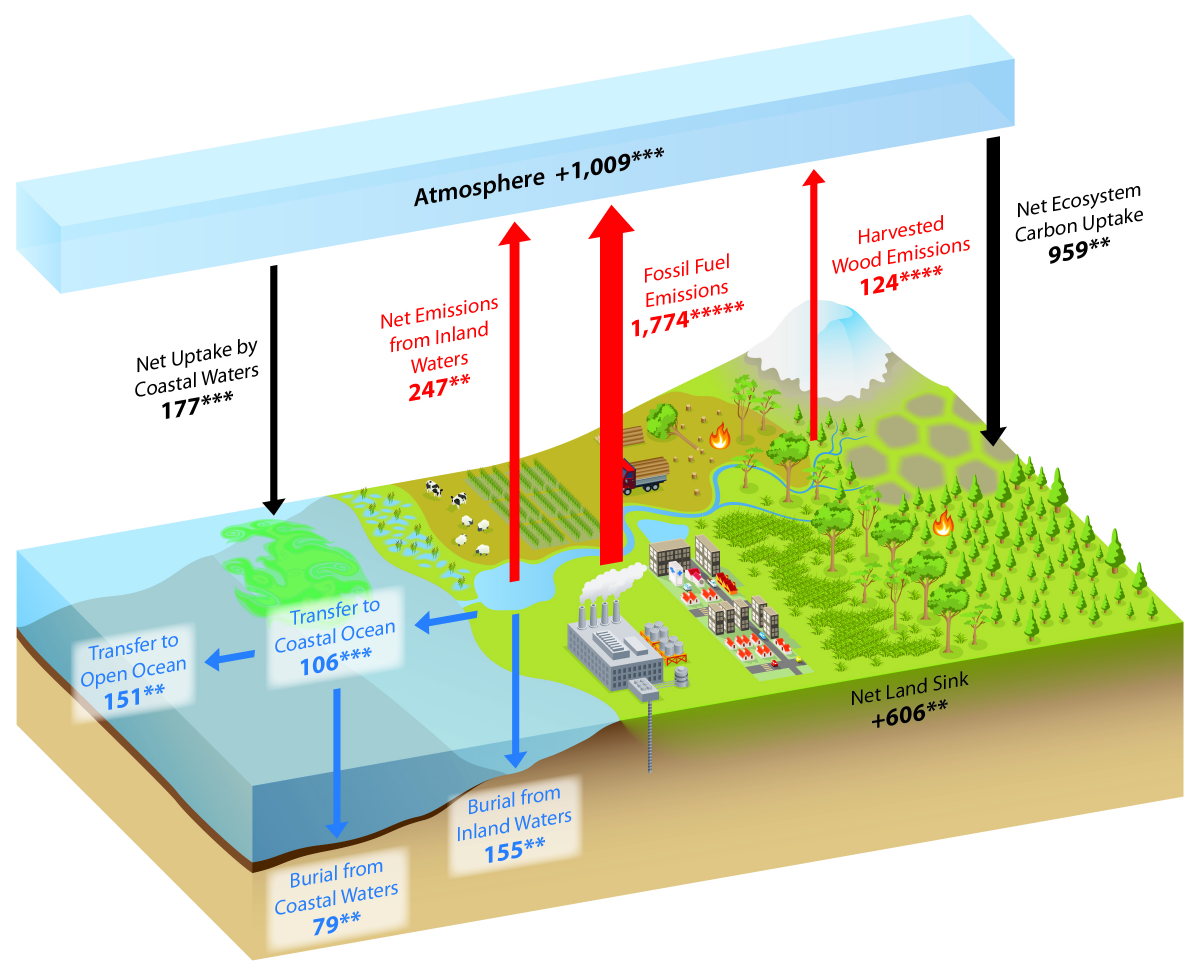
What Is The Carbon Cycle What Is The Science Behind It United States Carbon Cycle Science Program

Ecology 4 3 Carbon Cycling 4 4 Climate Change Flashcards Quizlet

Apes Unit 1 Flashcards Quizlet

Carbon Cycle Flashcards Quizlet

Climate Change Diagram Quizlet

Phosphorus Cycle Environmental Engineering Learning Science Rainforest Biome

Quizlet Live Carbon Cycle Flashcards Quizlet

Carbon Cylce Flashcards Quizlet

Chapter 17 Global Change Diagram Quizlet
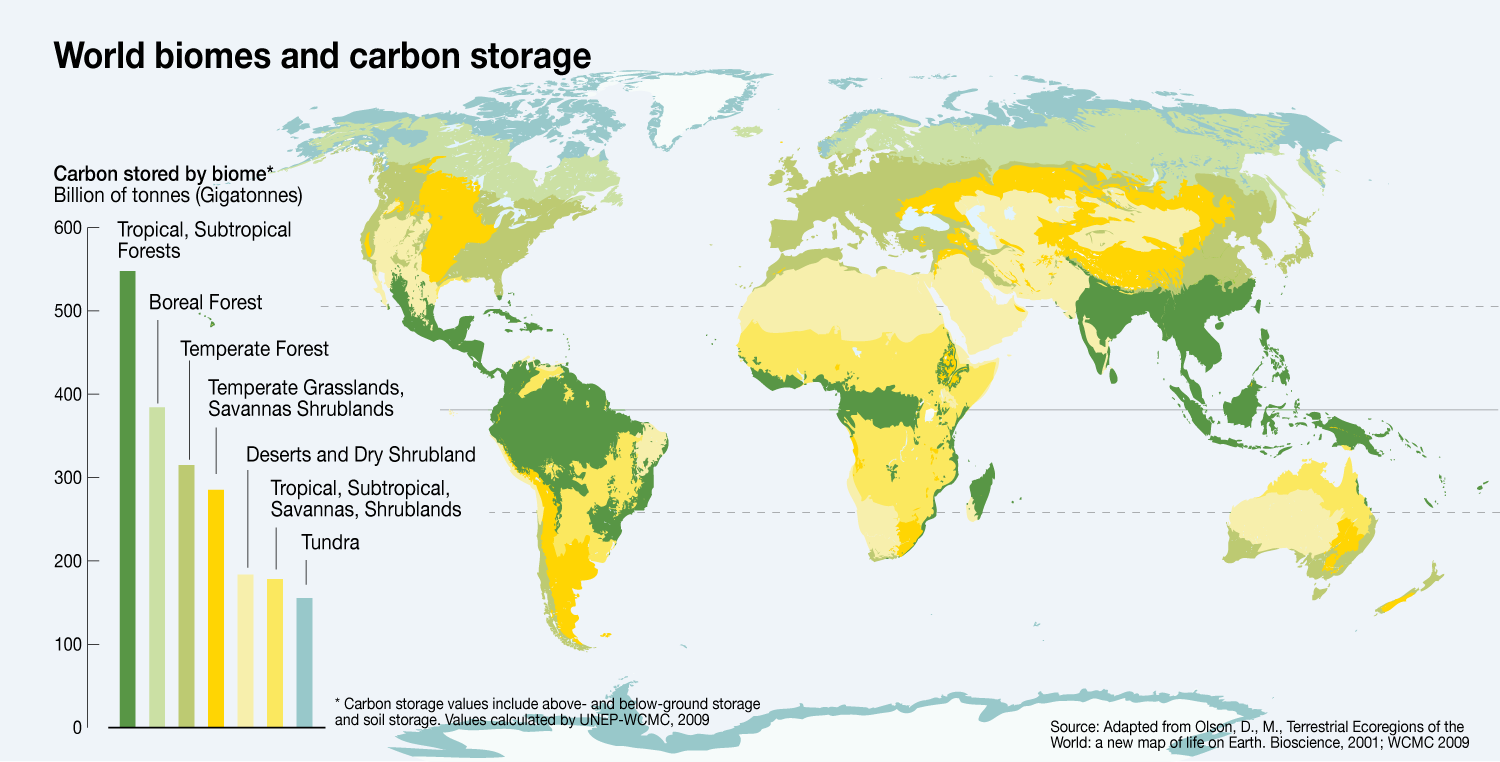
Ess Topic 7 3 Climate Change Mitigation And Adaptation Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green
Comments
Post a Comment